How to trim grape plants – Welcome to the world of viticulture! If you’re a budding grape grower, mastering the art of trimming grape plants is crucial for a bountiful harvest. This guide will take you through everything you need to know, from pruning techniques to disease management, empowering you to cultivate thriving vines that will produce the sweetest grapes.
Pruning Techniques: How To Trim Grape Plants
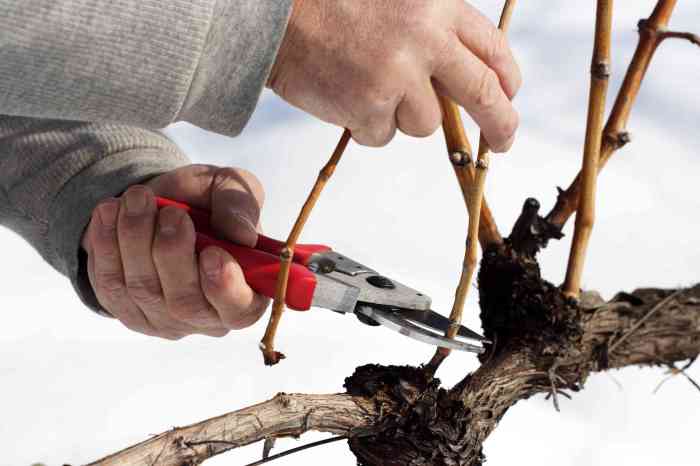

Pruning grape plants is a crucial viticultural practice that involves removing certain parts of the plant to enhance its growth, fruit production, and overall health. There are several pruning techniques employed in grape cultivation, each with its unique benefits and drawbacks.
The primary objective of pruning is to control the vine’s size and shape, promote new growth, and optimize fruit quality. By selectively removing canes, shoots, and leaves, pruners aim to create a balanced and productive vine that can withstand environmental stresses and produce high-quality grapes.
Cane Pruning
Cane pruning is a common technique used in vineyards worldwide. It involves selecting and retaining a specific number of canes (mature shoots from the previous season’s growth) on each vine. These canes are then shortened to a desired length, typically leaving 6-12 buds per cane.
Cane pruning promotes vigorous growth and fruit production, as it encourages the development of strong, upright canes that can support heavy fruit loads.
- Benefits:Enhances fruit production, promotes vine balance, and facilitates canopy management.
- Drawbacks:Requires careful selection of canes, can be labor-intensive, and may delay fruit production in young vines.
Guyot Pruning
Guyot pruning is a popular method used in regions with moderate climates. It involves retaining one or two canes, known as fruiting canes, on each vine. These canes are typically shortened to 2-4 buds, and a spur, which is a short shoot with 1-2 buds, is left near the base of the vine.
Trimming grape plants involves removing excess growth to promote fruit production. Similarly, trimming cordyline plants, as detailed in the guide at how to trim cordyline plants , focuses on removing dead or damaged leaves and encouraging new growth. By understanding the specific techniques for trimming both grape and cordyline plants, you can ensure optimal plant health and appearance.
Guyot pruning promotes early fruit production and produces high-quality grapes with good sugar levels.
- Benefits:Encourages early fruit production, simplifies canopy management, and improves fruit quality.
- Drawbacks:Requires precise pruning cuts, can be labor-intensive, and may reduce overall vine vigor.
Spur Pruning
Spur pruning is a technique that involves retaining short, stubby shoots, known as spurs, on the vine. These spurs typically have 2-3 buds, and they produce both fruiting canes and replacement spurs for the following season. Spur pruning is commonly used in regions with cold climates, as it protects the buds from winter damage and promotes early fruit production.
- Benefits:Protects buds from cold damage, promotes early fruit production, and simplifies canopy management.
- Drawbacks:Can reduce overall vine vigor, may require frequent pruning, and can limit fruit production in some varieties.
Head Pruning
Head pruning is a less common technique that involves cutting the vine back to a short stump, known as a head. This method is primarily used in regions with extremely cold climates, where it protects the vine from winter damage.
Head pruning encourages the development of new shoots from the base of the vine, which can then be trained and pruned to form a new canopy.
- Benefits:Protects vines from extreme cold, promotes new growth, and simplifies canopy management.
- Drawbacks:Delays fruit production, can reduce overall vine vigor, and may require extensive training and support.
Timing and Frequency of Pruning
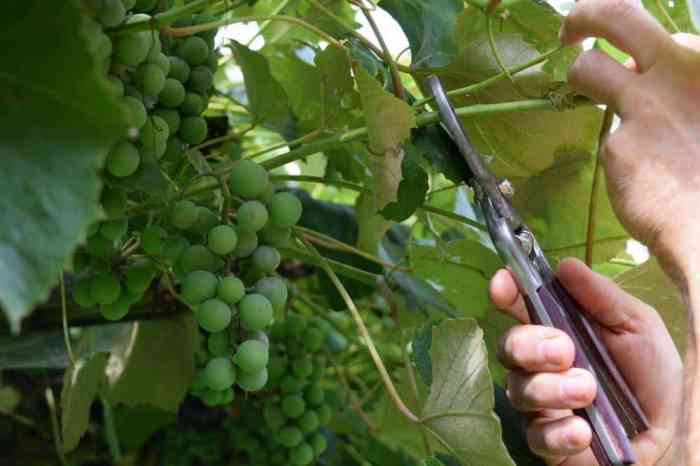

The optimal time to prune grape plants is during the dormant season, typically from late fall to early spring. Pruning at this time minimizes the risk of disease and allows the vines to recover before the growing season begins.
The frequency of pruning depends on the type of grapevine, the desired yield, and the climate. In general, vines that are grown for wine production require more frequent pruning than those grown for table grapes. In warm climates, pruning can be done more frequently to control vine growth and fruit production.
Factors Influencing Pruning Frequency
- Vine variety:Different grapevine varieties have different growth habits and require different pruning techniques.
- Climate:The climate can influence the frequency of pruning, as vines in warm climates may require more frequent pruning to control growth.
- Desired yield:Pruning can be used to control the yield of grapes. More frequent pruning can reduce yields, while less frequent pruning can increase yields.
- Vine age:Young vines require more frequent pruning than mature vines.
Determining When to Prune
The best time to prune grapevines is when the wood is dormant and the leaves have fallen. This typically occurs in late fall or early spring. Pruning at this time minimizes the risk of disease and allows the vines to recover before the growing season begins.
Tools and Equipment
Grape plant pruning requires specific tools and equipment to ensure efficient and precise cuts, minimizing damage to the vine and promoting optimal growth. Understanding the functions and benefits of each tool is crucial for successful pruning.
When trimming grape plants, it’s important to prune away dead or diseased canes. For blueberry plants, similar techniques apply. You’ll want to remove any weak or unproductive branches, encouraging new growth and fruit production. More detailed instructions on trimming blueberry plants can be found here . Returning to grape plants, remember to cut back laterals to a few buds to promote healthy growth.
Pruning Shears
- Bypass pruners: These feature two curved blades that pass by each other, making clean cuts on smaller branches up to 1 inch in diameter.
- Anvil pruners: These have one sharp blade that cuts against a flat anvil, suitable for larger branches up to 1.5 inches in diameter.
Loppers
- Handle loppers: Extendable handles provide reach and leverage for pruning branches up to 2 inches in diameter.
- Pole loppers: Attached to long poles, these enable pruning of higher branches without the need for ladders.
Saws
- Hand saws: Compact saws with curved blades for precise cuts on branches up to 4 inches in diameter.
- Bow saws: Larger saws with C-shaped frames, ideal for pruning thick branches up to 6 inches in diameter.
Other Tools
- Gloves: Protect hands from thorns and sharp edges.
- Pruning hooks: Curved blades for removing suckers and water sprouts.
- Sharpening stone: Essential for maintaining sharp blades.
Selection and Maintenance
Choosing the right tools depends on the size and age of the vines. Sharpen tools regularly to ensure clean cuts and prevent disease transmission. Store tools in a dry place to prevent rust and damage.
When it comes to trimming grape plants, the first step is to identify the dead or diseased canes. Once these are removed, you can focus on shaping the plant by cutting back the lateral shoots. If you’re also interested in trimming aloe plants, you can find a detailed guide on how to trim aloe plants . Returning to grape plants, it’s important to avoid over-trimming, as this can weaken the plant and reduce its fruit production.
Trellising Systems and Pruning
Trellising systems provide support for grapevines, improving their growth and productivity. Different trellising systems necessitate specific pruning techniques to optimize vine performance.
Vertical Trellising Systems
- Single Curtain Trellis:A single vertical wire supports vines trained to grow vertically, with laterals extending horizontally. Pruning focuses on maintaining a balance between vegetative growth and fruit production.
- Double Curtain Trellis:Two vertical wires support vines, with shoots trained in two vertical planes. Pruning aims to maintain a balanced canopy and control shoot density.
Horizontal Trellising Systems
- Tatura Trellis:Vines are trained along a horizontal wire, with shoots hanging vertically. Pruning focuses on shoot positioning and canopy management.
- Pergola Trellis:Vines are supported by a series of parallel wires, creating a shaded canopy. Pruning aims to maintain an open canopy and control shoot vigor.
Disease and Pest Management
Pruning plays a crucial role in preventing and controlling diseases and pests in grape plants. By removing infected or diseased plant material, pruning helps reduce the spread of pathogens and create a healthier growing environment. Additionally, proper pruning practices promote good air circulation, which helps prevent the development of fungal diseases and other moisture-related issues.
Specific Pruning Practices for Disease and Pest Control
- Powdery Mildew:Prune away infected leaves and shoots to prevent the spread of the fungus. Ensure good air circulation by opening up the canopy.
- Downy Mildew:Remove infected leaves and shoots promptly. Prune to improve air circulation and avoid overhead watering.
- Botrytis Bunch Rot:Prune away infected berries and remove excess foliage to improve air circulation and reduce humidity within the canopy.
- Grapevine Leafhoppers:Prune away infested leaves and shoots. Use reflective mulches to deter leafhoppers.
- Grape Berry Moth:Remove infested berries and prune away any dead or dying wood where the moth can overwinter.
Incorporating Disease and Pest Management into Pruning Strategies, How to trim grape plants
When pruning grape plants for disease and pest management, consider the following guidelines:
- Identify and Remove Infected Material:Regularly inspect plants for signs of disease or pests. Remove and dispose of infected plant material immediately to prevent the spread of pathogens or pests.
- Promote Air Circulation:Prune to open up the canopy and improve air circulation. This helps reduce moisture levels and prevents the development of fungal diseases.
- Avoid Overhead Watering:Water plants at the base to avoid wetting the leaves. Overhead watering can promote the development of fungal diseases.
- Sanitize Pruning Tools:Disinfect pruning tools between cuts to prevent the spread of diseases from one plant to another.
- Consider Resistant Varieties:Choose grape varieties that are resistant to common diseases and pests in your area.
By implementing these pruning practices, grape growers can effectively prevent and control diseases and pests, ensuring healthier and more productive vines.
Conclusive Thoughts

By following these comprehensive guidelines, you’ll be well-equipped to trim your grape plants with precision, ensuring their optimal health and productivity. Remember, the journey of a thousand grapes begins with a single trim. Embrace the knowledge shared here, and witness your grapevines flourish, rewarding you with an abundance of delectable fruit.
FAQs
When is the best time to prune grape plants?
The optimal time for pruning grape plants is during the dormant season, typically late winter or early spring, before the buds begin to swell.
What are the different pruning techniques for grape plants?
There are various pruning techniques for grape plants, including spur pruning, cane pruning, and cordon pruning. Each technique serves a specific purpose and is suitable for different trellising systems.
How often should I prune my grape plants?
The frequency of pruning depends on the grape variety, trellising system, and desired yield. Generally, grape plants require annual pruning to maintain their shape, productivity, and overall health.