How to remove unwanted plants from garden – Unwanted plants can be a nuisance in any garden, but there are several effective methods to remove them. From mechanical removal to chemical control, mulching, biological control, and cultural practices, this guide provides a comprehensive overview of how to keep your garden free of unwanted vegetation.
Understanding the different techniques and their applications will help you choose the best approach for your specific garden and plant needs. Whether you’re dealing with stubborn weeds or invasive species, this guide has the solutions you need to maintain a healthy and thriving garden.
Mechanical Removal Techniques
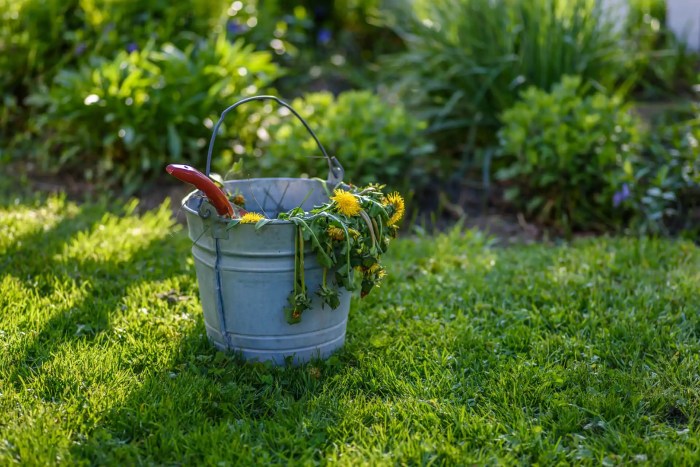

Eliminating unwanted plants manually is a cost-effective and eco-friendly method. It involves physically removing the plants by hand-pulling or digging them out.
Hand-pulling is suitable for small, shallow-rooted weeds. Grasp the plant firmly at its base and pull it straight up, ensuring to remove as much of the root system as possible. For larger or deeply rooted plants, digging tools like hoes, trowels, or weeders can be employed.
Preventing Damage to Desired Plants
During mechanical removal, it’s crucial to exercise caution to avoid damaging desired plants. Use tools with sharp edges to cleanly cut through weeds, and be mindful of the root systems of nearby plants. Consider using a weeding fork or hoe to loosen the soil around the unwanted plant before pulling it out, minimizing root disturbance to neighboring vegetation.
Chemical Control Methods
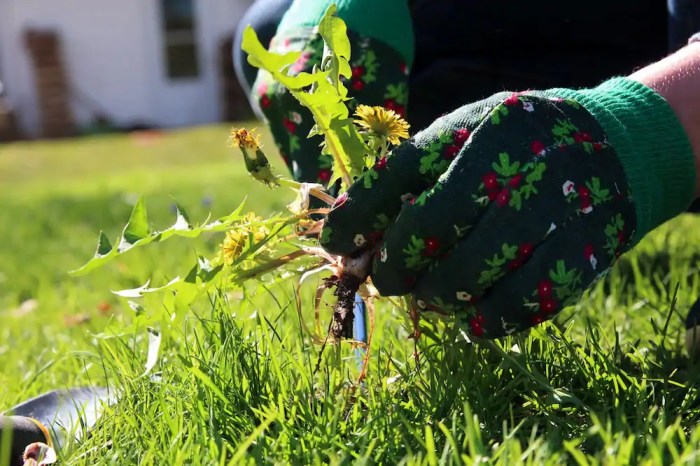

Chemical control methods involve the use of herbicides, which are chemical substances that kill or inhibit the growth of unwanted plants. Herbicides can be classified into two main groups: selective and non-selective.
Selective Herbicides, How to remove unwanted plants from garden
Selective herbicides target specific plant species or groups of plants, leaving desirable plants unharmed. They work by interfering with specific biochemical processes in the target plants, such as photosynthesis or cell division. Examples of selective herbicides include glyphosate, which is commonly used to control broadleaf weeds in lawns and gardens, and 2,4-D, which is used to control broadleaf weeds in crops.
Non-Selective Herbicides
Non-selective herbicides kill all plants they come into contact with, regardless of species. They are typically used in situations where complete vegetation control is desired, such as in industrial areas or along roadsides. Examples of non-selective herbicides include glyphosate and paraquat.
Choosing the Appropriate Herbicide
When choosing an herbicide, it is important to consider the following factors:
- The type of unwanted plant you are trying to control
- The location of the unwanted plants
- The presence of desirable plants in the area
- The environmental impact of the herbicide
It is always advisable to read and follow the label instructions carefully when using herbicides. Herbicides can be toxic to humans and animals if not used properly.
Mulching and Smothering Techniques
Mulching and smothering techniques are effective ways to control unwanted plant growth in the garden. Organic mulches, such as straw, bark, or compost, provide several benefits:
- Physical barrier:Mulches create a physical barrier that prevents unwanted plants from accessing sunlight and nutrients.
- Soil moisture regulation:Mulches help retain soil moisture, reducing the need for frequent watering and suppressing weed growth.
- Soil temperature moderation:Mulches insulate the soil, moderating soil temperature and creating a favorable environment for desirable plants.
- Soil enrichment:As mulches decompose, they add organic matter to the soil, improving its fertility and structure.
Proper Application and Maintenance of Mulches
When applying mulches, it is important to use a sufficient layer, typically 2-4 inches thick. Mulches should be spread evenly around plants, avoiding contact with stems or trunks. Regularly top up mulches as they decompose to maintain their effectiveness.Mulching is a cost-effective and environmentally friendly way to suppress unwanted plant growth in the garden.
By creating a physical barrier, altering soil conditions, and providing nutrients, mulches promote a healthy and thriving garden ecosystem.
To keep your garden looking its best, it’s important to remove unwanted plants regularly. This includes weeds, which can compete with your desired plants for water and nutrients. Pruning is another important gardening task, especially for plants that produce fruit or flowers.
For example, pruning strawberry plants in pots can help to increase fruit production and improve the overall health of the plants. Removing unwanted plants and pruning regularly will help to keep your garden healthy and productive.
Biological Control Options
Biological control is a method of controlling unwanted plants by introducing beneficial insects, microorganisms, or animals that feed on or compete with the target plants. This approach is considered environmentally friendly and can be a long-term solution for weed management.
Beneficial Insects
Insects like ladybugs, lacewings, and parasitic wasps can be released into the garden to control pests that damage plants. Ladybugs feed on aphids, lacewings consume whiteflies and mealybugs, and parasitic wasps lay eggs inside the bodies of caterpillars and other pests.
Microorganisms
Fungi and bacteria can also be used to control unwanted plants. Mycorrhizal fungi form symbiotic relationships with plant roots, helping them absorb nutrients and water while suppressing pathogens. Trichoderma is a fungus that attacks the roots of weeds, causing them to wilt and die.
Advantages of Biological Control
* Environmentally friendly
- Cost-effective in the long run
- Can provide long-term control
- Reduces the need for chemical pesticides
Limitations of Biological Control
* Can be slow to take effect
To keep your garden looking its best, removing unwanted plants is crucial. If you’re looking for a more detailed guide on plant maintenance, check out our article on how to trim bonsai plants . Returning to our topic, once you’ve cleared out the unwanted vegetation, you can focus on nurturing the desired plants and maintaining a thriving garden.
- Requires careful selection of control agents
- May not be effective against all types of weeds
- Can sometimes have unintended consequences
Cultural Practices for Prevention
Proper garden planning and maintenance are crucial for preventing unwanted plant growth. Implementing strategic techniques like crop rotation, companion planting, and maintaining healthy soil conditions can effectively minimize the establishment and spread of undesirable vegetation.
Crop Rotation
Crop rotation involves alternating different plant species in the same growing area over time. This practice helps break disease and pest cycles, improves soil health, and reduces the build-up of unwanted plant seeds in the soil.
Companion Planting
Companion planting involves strategically placing compatible plant species together. Certain plants can repel pests or inhibit the growth of unwanted plants through natural chemical interactions. For example, planting garlic near roses can deter aphids, while marigolds can repel nematodes.
Maintaining Healthy Soil Conditions
Maintaining healthy soil conditions by regularly adding organic matter, such as compost or manure, promotes microbial activity and improves soil structure. This makes it more difficult for unwanted plants to establish and compete with desirable vegetation.
Minimizing Seed Dispersal and Germination
To minimize seed dispersal and germination of unwanted plants, avoid overwatering, as excessive moisture can promote weed growth. Additionally, promptly remove unwanted plants before they go to seed to prevent seed spread. Regularly cleaning garden tools and equipment can also help prevent the accidental transfer of weed seeds from one area to another.
Unwanted plants can quickly overrun a garden, but removing them doesn’t have to be a chore. With a few simple steps, you can effectively eliminate these unwanted guests. One common garden plant that requires regular trimming is sage. For expert guidance on how to trim sage plants, visit this informative guide . After trimming your sage plants, you can continue removing unwanted plants in your garden, leaving it looking neat and tidy.
Summary: How To Remove Unwanted Plants From Garden

By implementing the strategies Artikeld in this guide, you can effectively remove unwanted plants from your garden and prevent their return. Remember to consider the specific needs of your garden and plants when selecting a removal method. With proper planning and maintenance, you can create a beautiful and vibrant garden free from unwanted vegetation.
FAQ Compilation
What is the most effective way to remove unwanted plants?
The most effective method depends on the specific plant and garden conditions. Manual removal is suitable for small infestations, while herbicides may be necessary for larger areas or persistent weeds.
How can I prevent unwanted plants from returning?
Regular maintenance, proper mulching, and crop rotation can help prevent unwanted plants from returning. Additionally, maintaining healthy soil conditions and minimizing seed dispersal can further reduce the risk of infestation.
Is it safe to use herbicides in my garden?
Herbicides can be effective for controlling unwanted plants, but it’s crucial to choose the right herbicide for your specific needs and follow the instructions carefully. Always prioritize safety and read the product label thoroughly before applying any chemicals.