How to cut the rose plant? This comprehensive guide will delve into the art and science of pruning rose plants, empowering you to cultivate vibrant and flourishing blooms. Whether you’re a novice gardener or an experienced horticulturist, this guide will provide invaluable insights into the techniques and benefits of proper pruning.
Pruning rose plants is not merely an aesthetic pursuit; it’s a crucial practice that promotes plant health, stimulates growth, and enhances flowering. By understanding the principles and techniques Artikeld in this guide, you’ll be able to confidently prune your rose plants, ensuring their longevity and maximizing their beauty.
Understanding Rose Plant Pruning
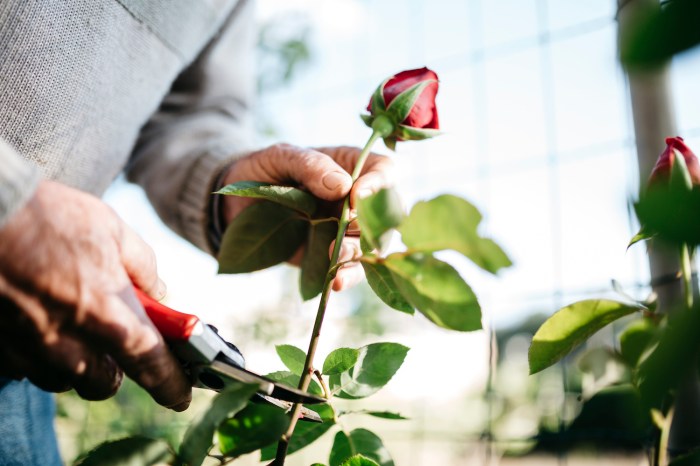

Pruning rose plants is an essential practice for maintaining their health, vigor, and beauty. It involves the strategic removal of selected stems, branches, or buds to achieve specific goals.
The primary benefits of pruning include:
- Enhancing plant growth and development by promoting new shoot production.
- Improving flowering by stimulating bud formation and increasing bloom size.
- Maintaining a balanced and aesthetically pleasing plant shape.
- Removing diseased or damaged plant material to prevent the spread of infections.
Types of Pruning Cuts, How to cut the rose plant
There are three main types of pruning cuts:
- Heading cut:A cut made at a node (the point where a leaf or branch joins the stem) to encourage branching and promote new growth.
- Thinning cut:A cut made to remove an entire branch or stem back to its point of origin, resulting in fewer but stronger canes.
- Deadheading:The removal of spent blooms to prevent seed formation and encourage continuous flowering.
Timing and Frequency of Pruning
The timing and frequency of pruning depend on the type of rose and its growth habit. Generally, roses are pruned in late winter or early spring before new growth begins.
Hybrid tea roses, for example, require annual pruning to maintain a compact shape and encourage vigorous flowering. Climbing roses, on the other hand, may only need pruning every few years to remove dead or damaged canes and maintain a manageable size.
Essential Tools and Techniques
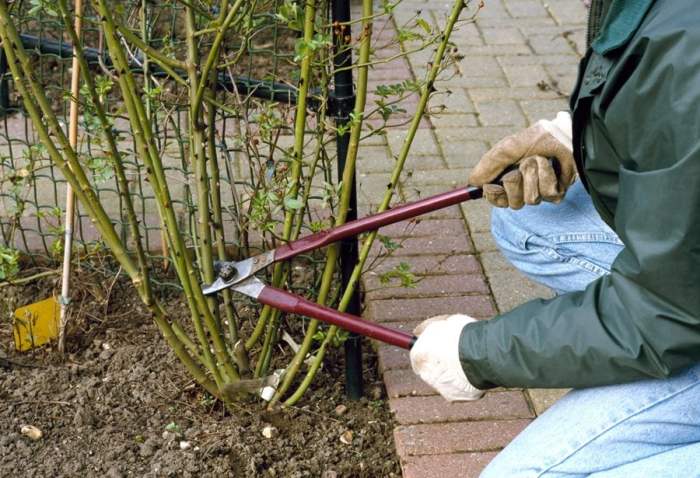

Essential tools for rose pruning include:
- Pruning shears: These are the most important tool for pruning roses. They should be sharp and well-maintained.
- Loppers: Loppers are used to remove larger branches.
- Hand saw: A hand saw is used to remove branches that are too large for loppers.
- Pruning gloves: Pruning gloves protect your hands from thorns.
- Safety glasses: Safety glasses protect your eyes from flying debris.
When pruning roses, it is important to use proper techniques. Here are some step-by-step instructions:
- Start by removing any dead, diseased, or damaged branches.
- Next, remove any branches that are crossing or rubbing against each other.
- Then, remove any suckers that are growing from the base of the plant.
- Finally, shape the plant by removing any branches that are too long or out of place.
Here are some diagrams to help you visualize the proper pruning techniques:
[Image of pruning diagrams]
Pruning for Specific Purposes
Pruning roses serves various purposes beyond basic maintenance. It promotes healthy growth, controls size, encourages flowering, and maintains the overall aesthetic appeal of the plant. Different types of roses require specific pruning techniques to achieve desired results.
Promoting Growth:To promote vigorous growth, prune young roses heavily in their first year. Remove weak and spindly canes, leaving only the strongest stems. This encourages the development of a strong framework and promotes new growth from the base of the plant.
Controlling Size:To control the size of roses, prune regularly to prevent them from becoming overgrown. For hybrid teas and floribundas, prune back to about 12-18 inches in late winter or early spring. Climbers can be pruned more severely to maintain their desired shape and size.
Encouraging Flowering:To encourage abundant flowering, deadhead spent blooms regularly. Remove the faded flowers by cutting just above the first set of five-leaflet leaves. This prevents the plant from putting energy into seed production and encourages the production of new flowers.
Removing Diseased or Damaged Canes:It is essential to remove any diseased or damaged canes promptly. Cut back to healthy wood, ensuring that all diseased or damaged tissue is removed. This prevents the spread of disease and promotes the overall health of the plant.
Pruning Different Types of Roses
Different types of roses have specific pruning requirements to maintain their optimal growth and flowering habits.
When pruning rose plants, it is essential to use sharp, clean shears to make precise cuts. This will help prevent disease and promote healthy growth. If you’re looking for inspiration on how to incorporate greenery into your home, check out 10 Hanging Plants Pinterest: Beautify Your Home with Greenery . It features a variety of beautiful and easy-to-care-for plants that can add a touch of nature to any space.
Returning to the topic of rose pruning, always remember to remove any dead or diseased canes and cut back overgrown stems to encourage new growth.
- Hybrid Teas:Prune hybrid teas heavily in late winter or early spring, removing up to two-thirds of the plant’s height. Cut back to a strong outward-facing bud.
- Floribundas:Prune floribundas less severely than hybrid teas, removing about one-third to one-half of the plant’s height. Focus on removing old or crossing canes.
- Climbers:Climbers require less frequent pruning, but it is important to remove any dead or diseased canes and train new canes to support the plant’s growth.
Advanced Pruning Techniques

Advanced pruning techniques, such as rejuvenation pruning and espaliering, are employed by experienced gardeners to enhance the health, appearance, and productivity of their rose plants. These methods require a deeper understanding of rose plant growth habits and pruning principles, but they can yield significant benefits when executed correctly.
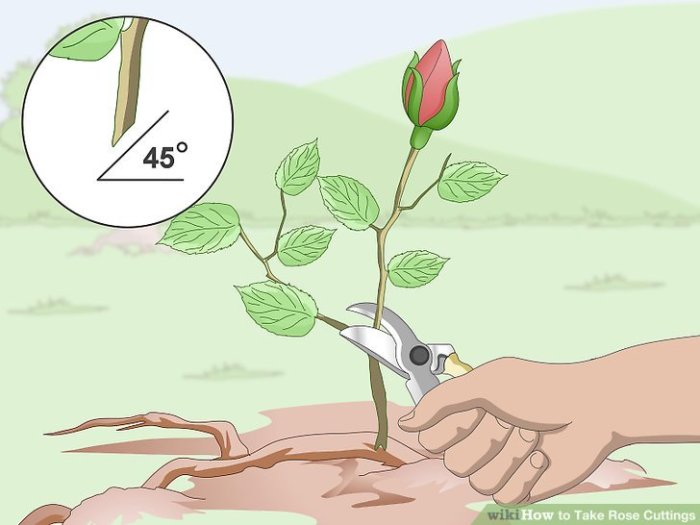
When cutting a rose plant, it is important to use sharp, clean shears to avoid damaging the stems. Cut the stems at a 45-degree angle, about 1/4 inch above a node. This will help the plant to absorb water and nutrients more easily.
For more tips on creating realistic greenery in your designs, check out 10 Hanging Plants Revit Family Free Download: Enhance Your Designs with Realistic Greenery . Additionally, remember to fertilize your rose plant regularly and prune it back in the spring to encourage new growth.
Rejuvenation Pruning
Rejuvenation pruning is a drastic pruning technique used to revitalize neglected or overgrown rose plants. It involves removing a significant portion of the plant’s old, unproductive wood to stimulate new growth. This technique is typically performed in late winter or early spring, when the plant is dormant.To
perform rejuvenation pruning, start by removing all dead, diseased, or damaged canes. Then, select several healthy canes that are at least two years old and cut them back to within 6-8 inches of the ground. Remove any remaining lateral branches from these canes.
The plant will then produce new shoots from the base, which will form the framework of the rejuvenated plant.
Espaliering
Espaliering is a pruning technique used to train rose plants to grow flat against a wall or fence. This method is often used for decorative purposes, as it creates a living wall or screen. Espaliering requires regular pruning to maintain the desired shape and size of the plant.To
To trim your rose plant, begin by removing any dead or diseased stems. If you’re looking for more plants and gardening supplies, check out plants bunnings . Once you’ve removed the dead stems, you can start shaping your plant. To do this, simply cut back the stems to the desired length.
Be sure to make clean cuts at a 45-degree angle.
espalier a rose plant, start by choosing a healthy, vigorous plant with strong, flexible canes. Plant the rose against the wall or fence and train the canes horizontally along wires or supports. Prune the canes regularly to encourage lateral growth and fill in the desired area.
Espaliering can be a challenging technique, but it can produce stunning results when done correctly.
Troubleshooting Pruning Problems
Pruning roses can be a rewarding task, but it’s essential to do it correctly to avoid problems. Here are some common pruning problems and how to fix them:
Over-Pruning
Over-pruning can weaken the rose plant and reduce its flowering potential. Signs of over-pruning include:
- Stunted growth
- Few or no flowers
- Weak, spindly canes
To correct over-pruning, gradually prune the plant back over several seasons. Start by removing no more than one-third of the plant’s growth each year. Gradually increase the amount of pruning each year until the plant has recovered.
Under-Pruning
Under-pruning can lead to a congested, overgrown rose plant that produces few flowers. Signs of under-pruning include:
- Dense, tangled growth
- Few or no new shoots
- Small, weak flowers
To correct under-pruning, prune the plant back more aggressively. Remove one-half to two-thirds of the plant’s growth, focusing on removing old, weak, or diseased canes. This will encourage new growth and flowering.
Improper Timing
Pruning roses at the wrong time of year can damage the plant and reduce its flowering potential. The best time to prune roses is in late winter or early spring, before new growth begins. Pruning at other times of the year can stress the plant and make it more susceptible to disease.
When pruning rose plants, it’s crucial to make clean cuts at a 45-degree angle. If you’re looking for ways to spruce up your living space, consider adding hanging plants. Check out 10 Hanging Plants to Elevate Your Rental Apartment for inspiration.
Remember, when cutting roses, always remove dead or diseased stems, and cut above a healthy bud facing outward.
Outcome Summary
In conclusion, mastering the art of how to cut the rose plant is a rewarding endeavor that will transform your rose bushes into thriving, bountiful spectacles. By following the guidance provided in this comprehensive guide, you’ll be equipped with the knowledge and skills to nurture healthy, vibrant rose plants that will grace your garden with their beauty for seasons to come.
Questions Often Asked: How To Cut The Rose Plant
Why is pruning rose plants important?
Pruning rose plants promotes plant health by removing dead or diseased canes, encouraging new growth, and improving air circulation. It also stimulates flowering, resulting in more abundant and vibrant blooms.
What are the different types of pruning cuts?
There are three main types of pruning cuts: heading cuts, thinning cuts, and renewal cuts. Heading cuts remove the top portion of a stem to encourage branching. Thinning cuts remove entire stems to improve air circulation and light penetration. Renewal cuts remove old or unproductive canes to promote new growth.
When is the best time to prune rose plants?
The best time to prune rose plants is in late winter or early spring, before new growth begins. This allows the plant to heal and recover before the growing season.
How often should I prune my rose plants?
Rose plants should be pruned annually to maintain their health and vigor. The frequency of pruning may vary depending on the type of rose and the desired results.