Does root rot go away – Unveiling the enigma of root rot, this comprehensive guide delves into the diagnosis, treatment, and preventive measures to safeguard your beloved plants from this detrimental ailment. Join us as we unravel the mysteries surrounding root rot, empowering you with the knowledge to combat this pervasive horticultural challenge.
Root Rot Identification
Root rot is a common problem that can affect plants of all types. It is caused by a variety of factors, including overwatering, poor drainage, and soil compaction. Root rot can be difficult to diagnose, as the symptoms can be similar to those of other plant problems.
However, there are a few key signs that can help you identify root rot:
- Yellowing or wilting leaves:This is one of the most common symptoms of root rot. The leaves may also become stunted or drop off prematurely.
- Soft or mushy roots:When you dig up a plant with root rot, the roots will be soft or mushy. They may also be discolored, or have a foul odor.
- Reduced growth:Plants with root rot will often have reduced growth, or may not grow at all.
If you suspect that your plant has root rot, it is important to take action immediately. The sooner you treat the problem, the better chance your plant has of surviving.
Causes of Root Rot
There are a number of factors that can cause root rot, including:
- Overwatering:Overwatering is one of the most common causes of root rot. When you overwater a plant, the roots do not have enough oxygen to breathe. This can lead to the development of root rot fungi.
- Poor drainage:Poor drainage can also lead to root rot. When water cannot drain away from the roots, it can create a stagnant environment that is ideal for the growth of root rot fungi.
- Soil compaction:Soil compaction can also contribute to root rot. When the soil is compacted, it can prevent water and oxygen from reaching the roots. This can create an environment that is favorable for the growth of root rot fungi.
In addition to these factors, root rot can also be caused by a number of other factors, including:
- Fungal infections:There are a number of different fungal infections that can cause root rot. These infections can be spread through the soil, water, or infected plants.
- Bacterial infections:Bacterial infections can also cause root rot. These infections are often spread through the soil or water.
- Nematodes:Nematodes are tiny roundworms that can also cause root rot. Nematodes feed on the roots of plants, which can damage the roots and make them more susceptible to infection.
Root Rot Treatment Options

Root rot, a fungal disease that affects the roots of plants, can be a serious problem for gardeners and farmers. If left untreated, root rot can lead to plant death. However, there are a number of treatment options available that can help to save infected plants.
Removing Infected Roots
One of the most effective ways to treat root rot is to remove the infected roots. This can be done by carefully digging up the plant and removing the damaged roots. Once the infected roots have been removed, the plant should be replanted in a well-drained location.
Improving Drainage
Improving drainage is another important step in treating root rot. This can be done by amending the soil with organic matter, such as compost or peat moss. Organic matter helps to improve drainage by increasing the amount of air in the soil.
Root rot, a fungal disease that affects the roots of plants, can be a serious problem for corn plants. If left untreated, root rot can lead to the death of the plant. However, with proper care, it is possible to prevent or treat root rot in corn plants.
Corn plant care includes providing the plant with well-drained soil, watering it regularly, and fertilizing it according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Additionally, it is important to avoid overwatering the plant, as this can create conditions that are favorable for the development of root rot.
It also helps to hold water, which can help to prevent the soil from becoming waterlogged.
Fungicides and Other Chemical Treatments
Fungicides can be used to treat root rot, but they should only be used as a last resort. Fungicides can be harmful to plants, and they can also be harmful to the environment. If you decide to use a fungicide, be sure to follow the directions on the label carefully.
Case Studies
There are a number of case studies that have shown that root rot can be successfully treated. In one study, researchers were able to save a group of tomato plants that were infected with root rot by removing the infected roots and improving drainage.
In another study, researchers were able to save a group of corn plants that were infected with root rot by using a fungicide.
Preventing Root Rot
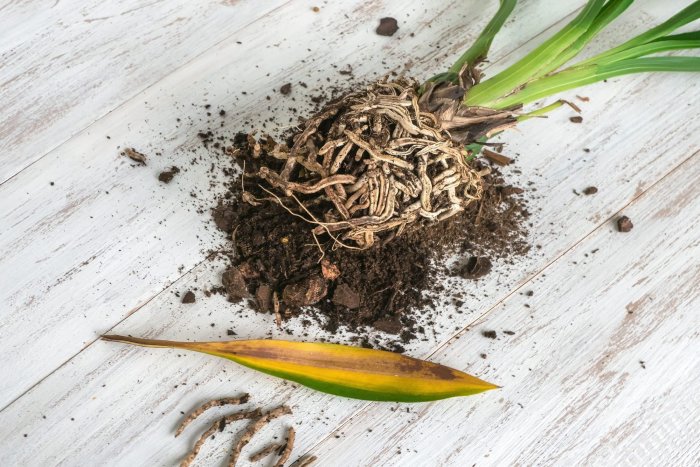

Root rot is a common problem that can affect plants of all types. It is caused by a fungus that thrives in moist, poorly-drained soil. Root rot can cause plants to wilt, yellow, and eventually die. Fortunately, there are a number of things you can do to prevent root rot from developing in your plants.
Proper Watering Practices
One of the most important things you can do to prevent root rot is to avoid overwatering your plants. When you water your plants, make sure to only water them until the soil is moist to the touch. Do not water your plants so much that the water runs out of the bottom of the pot.
Unfortunately, root rot cannot be reversed once it sets in. To prevent this issue in the future, it’s crucial to provide optimal care for your Elephant Ear plant, as outlined in our comprehensive guide on how to care for elephants ear plant . By following these expert recommendations, you can ensure your plant thrives and avoid the devastating effects of root rot.
Well-Draining Soil
Another important factor in preventing root rot is to use well-draining soil. Well-draining soil allows water to drain away from the roots of your plants, which helps to prevent the soil from becoming waterlogged. You can improve the drainage of your soil by adding sand or perlite to it.
Proper Pot Size
The size of the pot you use can also affect the development of root rot. If the pot is too small, the roots of your plant will become cramped and may not be able to get enough oxygen. This can make your plant more susceptible to root rot.
Root rot, a common issue among plants, can be a persistent problem. While some plants may recover with proper care, others may succumb to the infection. The silver lace fern , known for its delicate foliage, is particularly susceptible to root rot.
However, with prompt attention and proper treatment, it is possible to save affected plants and prevent further spread of the disease.
Choose a pot that is large enough to accommodate the roots of your plant, but not so large that the soil stays wet for too long.
Aeration, Does root rot go away
Aeration is also important for preventing root rot. Aeration allows air to circulate around the roots of your plants, which helps to keep them healthy. You can improve the aeration of your soil by adding compost or other organic matter to it.
Key Steps for Preventing Root Rot
The following table summarizes the key steps for preventing root rot:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Avoid overwatering your plants. |
| 2 | Use well-draining soil. |
| 3 | Choose a pot that is large enough to accommodate the roots of your plant. |
| 4 | Improve the aeration of your soil. |
Root Rot Resistance
Root rot resistance is a plant’s ability to withstand or tolerate infection by root rot pathogens. Plants may exhibit varying levels of resistance, from complete immunity to susceptibility. Resistance mechanisms can include physical barriers, biochemical defenses, and genetic factors.
Certain plant species have evolved natural resistance to root rot. For example, some tomato varieties possess a gene called Rpi-blb, which confers resistance to the soil-borne fungus Fusarium oxysporum, a common cause of root rot in tomatoes.
Breeding and Developing Root Rot-Resistant Plants
Research and breeding efforts are ongoing to develop new plant varieties with enhanced root rot resistance. Plant breeders use genetic techniques to introduce resistance genes from wild or resistant cultivars into commercial varieties. For instance, scientists have developed soybean varieties with resistance to Phytophthora sojae, a fungus that causes root rot in soybeans.
Root Rot in Different Plant Types: Does Root Rot Go Away
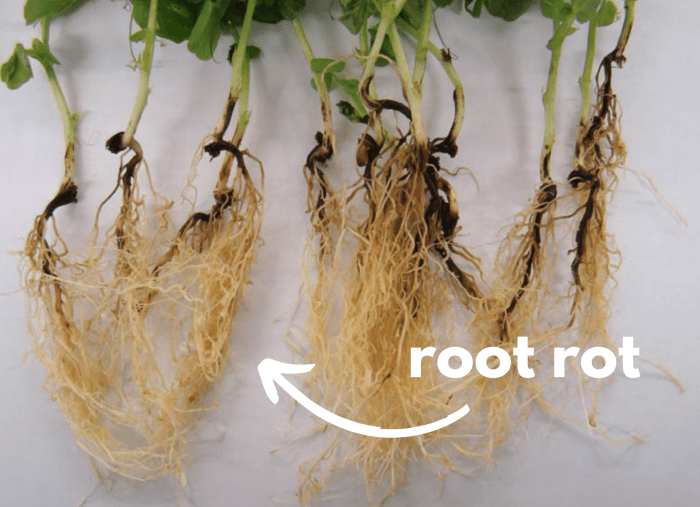
Root rot, a devastating disease caused by fungal pathogens, affects a wide range of plant species, including vegetables, flowers, and trees. The symptoms and treatments for root rot vary depending on the type of plant affected.
Vegetables
In vegetables, root rot often manifests as stunted growth, yellowing leaves, and wilting. The roots may appear brown or black and have a mushy texture. Common fungal pathogens responsible for root rot in vegetables include Pythiumand Rhizoctonia. Treatment involves improving drainage, using resistant varieties, and applying fungicides.
Flowers
Root rot in flowers can cause wilting, yellowing, and stunted growth. The roots may become soft and discolored. Common fungal pathogens include Phytophthoraand Fusarium. Treatment options include adjusting watering practices, removing infected plants, and applying fungicides.
Trees
Trees affected by root rot may exhibit symptoms such as leaf discoloration, premature leaf drop, and reduced growth. The roots may be decayed and have a foul odor. Common fungal pathogens include Armillariaand Ganoderma. Treatment involves improving drainage, removing infected trees, and using fungicides.
| Plant Type | Symptoms | Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Vegetables | Stunted growth, yellowing leaves, wilting, brown/black mushy roots | Improve drainage, use resistant varieties, apply fungicides |
| Flowers | Wilting, yellowing, stunted growth, soft/discolored roots | Adjust watering, remove infected plants, apply fungicides |
| Trees | Leaf discoloration, premature leaf drop, reduced growth, decayed roots with foul odor | Improve drainage, remove infected trees, apply fungicides |
Case Study: Root Rot in Tomato Plants
In a recent case study, a tomato grower experienced severe root rot in their greenhouse. The affected plants exhibited stunted growth, yellowing leaves, and wilting. Examination of the roots revealed brown, mushy discoloration, indicating Pythiuminfection. The grower implemented a comprehensive treatment plan involving improved drainage, application of a fungicide, and removal of infected plants.
As a result, the root rot outbreak was successfully controlled, and the tomato plants recovered.
Epilogue
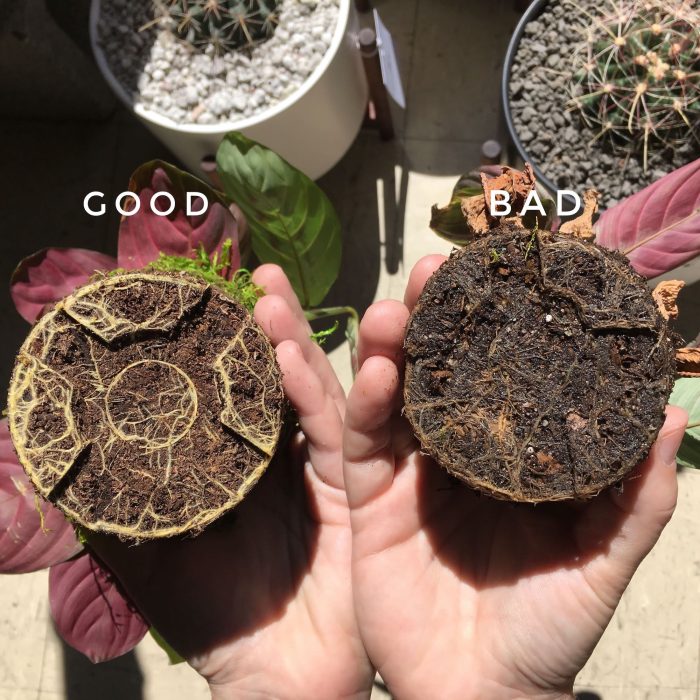

In the realm of horticulture, root rot stands as a formidable adversary, threatening the health and vitality of our cherished plants. Yet, armed with the insights gleaned from this exhaustive guide, you possess the tools to effectively combat this pervasive ailment.
Remember, vigilance, early detection, and proactive measures are your allies in the battle against root rot. By adhering to the principles Artikeld herein, you can cultivate a thriving garden, where vibrant blooms and bountiful harvests flourish, unmarred by the insidious grip of root rot.
Question & Answer Hub
Can root rot be reversed?
While advanced stages of root rot may be irreversible, early detection and prompt treatment can significantly improve the chances of plant recovery.
How can I tell if my plant has root rot?
Signs of root rot include yellowing leaves, wilting, stunted growth, and soft, mushy roots.
What causes root rot?
Overwatering, poor drainage, and fungal infections are common causes of root rot.