Best plants erosion control – Erosion control is crucial for maintaining the health and stability of our environment. Plants play a vital role in this process, offering a natural and effective solution to combat soil erosion. This comprehensive guide explores the best plants for erosion control, empowering you to make informed choices for your land.
From deep-rooted grasses to dense shrubs, we delve into the characteristics that make certain plant species particularly effective in erosion control. Discover the specific benefits and limitations of each plant, including their growth habits, maintenance requirements, and potential drawbacks.
Identify Effective Plant Species for Erosion Control
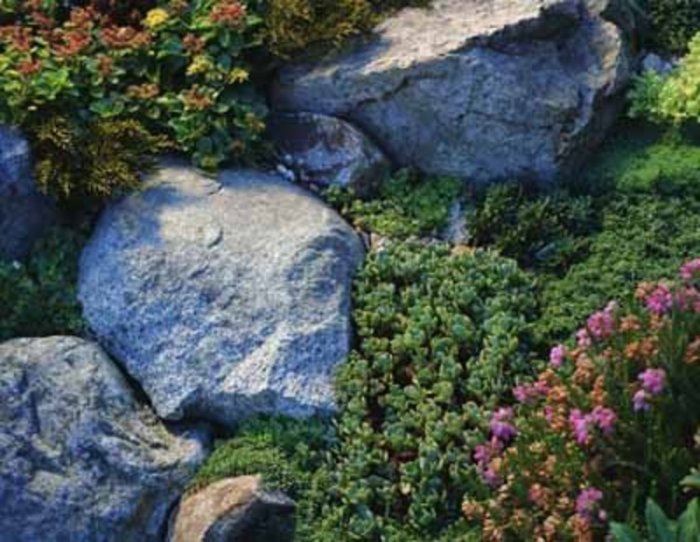

Plant species play a vital role in erosion control, preventing soil loss and stabilizing slopes. Their extensive root systems bind the soil, while their dense foliage intercepts rainfall and reduces runoff velocity. This comprehensive list presents proven plant species with specific characteristics that make them suitable for erosion control.
Woody Plants
- Willow (Salixspp.) : Rapidly growing trees with extensive root systems that stabilize riverbanks and other wet areas.
- Poplar (Populusspp.) : Deciduous trees with deep roots and dense foliage that provide excellent windbreaks and erosion control.
- Alder (Alnusspp.) : Nitrogen-fixing trees with strong root systems that thrive in moist soils and help prevent bank erosion.
Grasses
- Vetiver Grass (Chrysopogon zizanioides) : A tall, clump-forming grass with a dense root system that is highly effective in controlling soil erosion on slopes.
- Bermuda Grass (Cynodon dactylon) : A warm-season grass with a dense, spreading root system that forms a thick mat, preventing soil erosion.
- Reed Canary Grass (Phalaris arundinacea) : A tall, wetland grass with a fibrous root system that stabilizes stream banks and other wet areas.
Groundcovers
- Creeping Jenny (Lysimachia nummularia) : A low-growing, spreading groundcover with shallow roots that forms a dense mat, preventing erosion on slopes and in shady areas.
- Periwinkle (Vinca minor) : An evergreen groundcover with a shallow, fibrous root system that creates a dense cover, suppressing weeds and preventing erosion.
- Pachysandra (Pachysandra terminalis) : A shade-tolerant groundcover with a shallow root system that forms a dense mat, preventing erosion and suppressing weeds.
Other Species
- Sedges (Carexspp.) : Grass-like plants with fibrous root systems that stabilize stream banks and other wet areas.
- Rushes (Juncusspp.) : Grass-like plants with dense, fibrous root systems that tolerate wet and saline conditions, making them suitable for erosion control in coastal areas.
Design Erosion Control Strategies Using Plants

Erosion control is crucial for preserving soil health, preventing infrastructure damage, and maintaining ecosystem stability. Plants play a vital role in mitigating erosion by providing physical barriers, absorbing rainfall, and enhancing soil stability.
Planting Techniques and Strategies
Effective erosion control strategies involve selecting appropriate plant species, determining optimal plant spacing and density, and employing suitable planting techniques. Different erosion scenarios require specific approaches:
- Slopes:Plant perpendicular to the slope to slow down water flow and prevent soil loss. Consider using groundcovers, shrubs, or trees with deep root systems.
- Riverbanks:Establish vegetation along riverbanks to protect against scour and flooding. Select species that tolerate fluctuating water levels and root deeply to stabilize the soil.
- Construction Sites:Implement temporary erosion control measures during construction, such as seeding or mulching exposed areas. Utilize erosion control blankets or matting to prevent soil displacement.
Plant Spacing and Density
Optimal plant spacing and density vary depending on the erosion severity, soil conditions, and plant species. Closer spacing and higher density provide better erosion control, but it’s essential to avoid overcrowding to prevent competition for resources.
Species Selection
Selecting suitable plant species is crucial for successful erosion control. Consider factors such as:
- Root Structure:Deep-rooted species anchor soil and prevent erosion.
- Growth Habit:Spreading groundcovers or dense shrubs provide a protective barrier.
- Erosion Tolerance:Choose species that can withstand erosion forces and establish quickly.
Compare and Contrast Plant-Based Erosion Control Methods
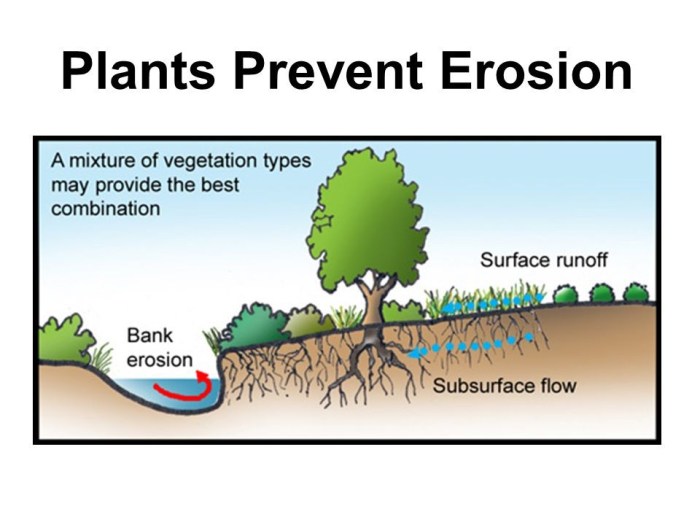
Plant-based erosion control methods, which involve using vegetation to stabilize soil and prevent erosion, offer several advantages and disadvantages compared to other erosion control techniques.
Cost-Effectiveness
Plant-based methods are generally more cost-effective than other methods, such as geotextiles or riprap, in the long run. While the initial cost of planting vegetation may be higher, it requires less maintenance and replacement costs over time.
Environmental Impact, Best plants erosion control
Plant-based methods have a lower environmental impact than other erosion control techniques. Vegetation helps improve soil quality, provides habitat for wildlife, and filters pollutants from water. In contrast, geotextiles and riprap can be visually intrusive and may hinder the growth of native vegetation.
Among the best plants for erosion control are creeping juniper, beach grass, and buffalo grass. For further guidance on selecting and caring for indoor plants, refer to Discover the Allure of Indoor Plant Stores: A Guide to Greenery and Decor . Additionally, consider planting a variety of these erosion-control plants to create a resilient landscape.
Long-Term Sustainability
Plant-based erosion control methods are more sustainable in the long term. Vegetation can adapt to changing environmental conditions and provide ongoing erosion protection. Geotextiles and riprap, on the other hand, may deteriorate over time and require replacement.
Appropriate Situations
Plant-based erosion control methods are most appropriate in areas with gentle slopes and moderate erosion potential. They are also suitable for areas where vegetation can be easily established and maintained. Alternative approaches, such as geotextiles or riprap, may be necessary in areas with steep slopes, high erosion potential, or where vegetation cannot be easily established.
Create an Erosion Control Plan Using Plantings

Erosion control is crucial for preserving soil, water quality, and infrastructure. Using plants is a sustainable and effective way to combat erosion, and creating a well-crafted erosion control plan is essential for success.
Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you create an erosion control plan that incorporates plant-based solutions:
Site Assessment
Thoroughly assess the site to identify areas prone to erosion, including slopes, drainage channels, and areas with exposed soil. Consider factors such as soil type, vegetation cover, and hydrology.
For effective erosion control, consider plants with dense root systems and foliage that can withstand environmental stressors. One such plant is the Ribbon Fern ( Ribbon Fern: An Enduring Beauty Unveiled ), known for its resilience and ability to thrive in various conditions.
Its adaptability and low-maintenance nature make it a valuable addition to erosion control strategies, alongside other recommended plants for this purpose.
Erosion Risk Identification
Determine the potential for erosion based on the site assessment. Consider factors such as rainfall intensity, slope angle, and soil erodibility. Identify areas where erosion is likely to occur and prioritize them for plant-based erosion control measures.
Plant Species Selection
Choose plant species that are well-suited to the site conditions and erosion risks. Consider factors such as root depth, canopy cover, and ability to tolerate erosion. Native plant species are often preferred as they are adapted to local conditions.
For optimal erosion control, consider employing plants with extensive root systems that can effectively bind soil and prevent erosion. Hanging plants, like ivy or ferns , can also contribute to erosion control by providing ground cover and preventing soil loss on slopes or areas with limited vegetation.
These plants help maintain soil stability, reduce runoff, and promote healthy ecosystems.
Planting Strategies
Determine the appropriate planting strategies based on the site conditions and plant species selected. Consider factors such as planting density, spacing, and soil amendments. Use a variety of planting techniques, such as seeding, container planting, and live staking, to maximize effectiveness.
Maintenance and Monitoring
Regular maintenance is crucial to ensure the effectiveness of the erosion control plan. Monitor plant growth, soil stability, and erosion potential. Conduct regular inspections and implement maintenance measures such as watering, fertilizing, and weed control as needed.
Best plants erosion control should be resilient, tolerant to extreme weather, and have strong root systems to hold the soil in place. To keep these plants healthy and thriving, refer to Spots on Plant: A Comprehensive Guide to Identification Prevention and Treatment for guidance on identifying and treating common plant diseases and pests that can weaken plants and compromise their ability to control erosion.
Showcase Successful Plant-Based Erosion Control Projects: Best Plants Erosion Control
Plant-based erosion control methods have proven successful in numerous projects, demonstrating their effectiveness in combating soil erosion and enhancing environmental health. These projects exemplify the benefits of utilizing plants to stabilize slopes, reduce sediment runoff, and restore degraded landscapes.
One notable example is the restoration of the degraded hillsides in the San Francisco Bay Area, California. The project involved planting native grasses, shrubs, and trees to stabilize the slopes and prevent further erosion. The plant cover effectively reduced soil loss and improved water infiltration, leading to the restoration of the natural ecosystem and enhanced biodiversity.
Cost Savings and Environmental Restoration
Plant-based erosion control offers significant cost savings compared to traditional methods like concrete or riprap. Plants require minimal maintenance and can self-propagate over time, reducing long-term expenses. Additionally, plant cover improves soil health, enhances water quality, and provides habitat for wildlife, contributing to overall environmental restoration.
Aesthetic Appeal and Community Engagement
Beyond their practical benefits, plant-based erosion control projects also enhance the aesthetic appeal of landscapes. Native plant species can create visually pleasing environments, attract pollinators, and provide recreational opportunities for communities. By involving local residents in planting and maintenance efforts, these projects foster a sense of ownership and stewardship.
Last Word
Whether you’re facing erosion on slopes, riverbanks, or construction sites, this guide provides practical strategies for using plants to mitigate erosion effectively. By understanding the principles of erosion control and the unique capabilities of different plant species, you can create a customized erosion control plan that meets your specific needs.
Embrace the power of plants to protect your land, restore ecosystems, and enhance the beauty of your surroundings. Invest in erosion control today for a sustainable and resilient future.
FAQ Section
What are the most effective plants for erosion control on slopes?
Grasses with deep root systems, such as fescues and ryegrasses, are ideal for stabilizing slopes. Shrubs like willows and dogwoods provide additional support and help reduce runoff.
How do plants help control erosion?
Plants’ root systems anchor the soil, preventing it from being washed away by wind or water. Their dense foliage slows down runoff and traps sediment.
What are the advantages of using plants for erosion control?
Plant-based erosion control is cost-effective, environmentally friendly, and aesthetically pleasing. Plants improve soil health, provide habitat for wildlife, and enhance biodiversity.