How to trim a plant – Trimming plants is an essential gardening practice that can enhance their health, appearance, and productivity. This comprehensive guide will provide you with all the knowledge and techniques you need to master the art of plant trimming, ensuring your plants thrive and bring joy to your surroundings.
Understanding the purpose and benefits of trimming, the different types of plant growth, and the optimal time to trim are crucial steps in achieving successful results. This guide will delve into these aspects and provide practical tips to help you make informed decisions.
Understanding Plant Trimming

Trimming plants, a crucial horticultural practice, involves removing unwanted or excess plant material to optimize growth, health, and appearance. It promotes the plant’s overall vigor, productivity, and aesthetic appeal.
Different plant species exhibit distinct growth patterns, influencing the frequency and techniques of trimming. Some plants, like herbaceous annuals, require regular trimming to maintain their compact shape and encourage flowering. Conversely, woody perennials, such as trees and shrubs, may need less frequent trimming, primarily to remove dead or diseased branches and shape the plant’s form.
Trimming plants is an essential part of plant care, promoting healthy growth and aesthetics. Whether you’re a seasoned plant enthusiast or just starting out, proper trimming techniques can significantly enhance the vitality of your greenery. For inspiration, consider incorporating hanging plants into your space.
10 Hanging Plants to Elevate Your Rental Apartment offers a curated selection of low-maintenance and visually stunning options to transform your living area. Remember, regular trimming not only improves plant health but also maintains a pleasing appearance, ensuring your plants thrive and bring joy to your home.
Optimal Trimming Time
Determining the optimal time to trim plants depends on several factors, including the plant species, its growth stage, and the desired outcome. Generally, it’s best to trim during the plant’s dormant period, when growth is naturally slower. This minimizes stress on the plant and allows it to recover more easily.
For spring-blooming plants, trimming is typically done in late winter or early spring, before new growth begins. For summer-blooming plants, it’s best to trim after they have finished flowering to encourage new growth and flowering the following year.
Trimming plants is essential for their health and appearance. Removing dead or overgrown leaves and stems promotes new growth and keeps the plant looking its best. For more inspiration on how to enhance your indoor space with greenery, check out 10 Hanging Plants Pinterest: Beautify Your Home with Greenery . This article showcases stunning hanging plants that can add a touch of nature and elegance to any room.
By following these simple trimming tips and exploring the hanging plant ideas in the article, you can create a lush and inviting indoor environment.
Tools and Techniques for Trimming
The art of plant trimming requires a selection of essential tools and a keen understanding of proper techniques to achieve precise and effective results. This section delves into the necessary equipment and demonstrates the appropriate use of pruning shears, loppers, and other tools to ensure optimal plant health and aesthetics.
Essential Tools for Plant Trimming
- Pruning Shears:These handheld shears feature sharp blades designed for precise cutting of small branches and stems.
- Loppers:Long-handled shears with larger blades, ideal for cutting thicker branches and limbs.
- Hand Saw:A small saw used for removing larger branches or trunks.
- Trimming Knife:A sharp knife used for delicate cuts and shaping.
Proper Techniques for Using Pruning Tools
Using the correct technique is crucial to avoid damaging plants or transmitting diseases. Here are the key steps:
- Identify the Cutting Point:Determine the exact location where the cut should be made, considering the plant’s growth pattern and desired shape.
- Sterilize Tools:Disinfect pruning tools with rubbing alcohol or a bleach solution to prevent disease transmission.
- Make a Clean Cut:Use sharp, clean blades to make a clean, angled cut that slopes away from the bud or branch you are retaining.
- Avoid Over-Trimming:Remove only the necessary branches or leaves to maintain the plant’s health and shape.
Methods of Trimming
Trimming plants involves various methods, each with specific techniques and goals. Understanding these methods allows gardeners to effectively manage plant growth and aesthetics.
For proper plant growth, it is important to trim them occasionally to remove dead or damaged leaves. When trimming, use sharp, clean shears to make precise cuts. To enhance your plant designs with realistic greenery, check out 10 Hanging Plants Revit Family Free Download: Enhance Your Designs with Realistic Greenery for a collection of Revit family downloads.
This resource provides a wide range of hanging plant models that can add a touch of nature to your projects. Once you have the models, you can easily trim and arrange them to create stunning plant displays.
Deadheading, How to trim a plant
Deadheading involves removing spent flowers or flower heads to encourage new growth and flowering. It prevents plants from putting energy into seed production and promotes continuous blooming. Techniques include pinching off faded flowers by hand or using sharp shears to cut back flower stems to the nearest leaf node.
Thinning
Thinning removes excess stems or branches to improve air circulation and light penetration. It reduces overcrowding and allows remaining stems to grow stronger and healthier. Techniques include selectively pruning out weak or diseased stems, removing suckers or water sprouts, and thinning out dense foliage to promote better airflow.
When trimming a plant, it’s important to use sharp, clean shears to avoid damaging the stems. For real hanging plants , trim back any dead or dying leaves, and prune stems that are too long or unruly. This will help to keep your plant healthy and looking its best.
Shaping
Shaping involves trimming plants to achieve a desired form or size. It is commonly used for hedges, topiaries, and ornamental trees. Techniques include pruning branches to create specific shapes, shearing to maintain a uniform size, and selectively removing branches to open up the plant’s interior and improve light distribution.
| Method | Goal | Techniques |
|---|---|---|
| Deadheading | Promote new growth and flowering | Pinching off faded flowers, cutting back flower stems |
| Thinning | Improve air circulation and light penetration | Removing weak or diseased stems, suckers, thinning out dense foliage |
| Shaping | Achieve desired form or size | Pruning branches to create shapes, shearing to maintain size, removing branches to open up interior |
Specific Plant Care
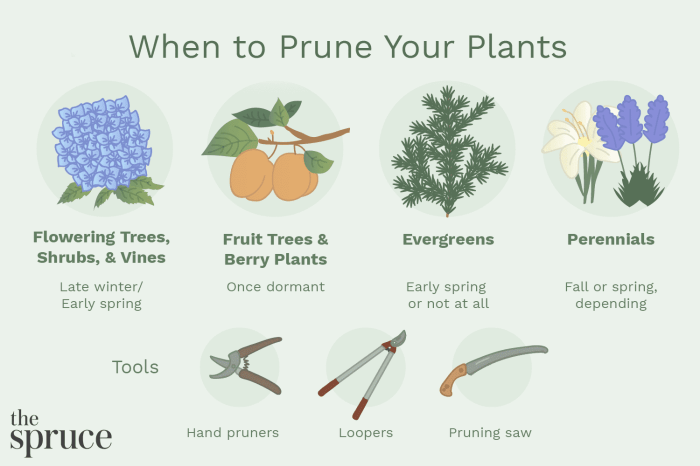
Trimming requirements vary greatly depending on the type of plant. Here’s a breakdown of specific trimming needs for different plant categories:
Trees
- Evergreen Trees:Prune lightly to remove dead or diseased branches and maintain shape. Avoid heavy pruning, as it can damage the tree’s natural form.
- Deciduous Trees:Prune during dormancy to encourage new growth and remove weak or crossing branches. Pruning techniques vary depending on the tree species.
Shrubs
- Flowering Shrubs:Prune after blooming to encourage next season’s flowering. Remove dead or overgrown branches to maintain a compact shape.
- Evergreen Shrubs:Prune lightly throughout the year to maintain shape and remove any diseased or damaged branches.
Flowers
- Perennial Flowers:Deadhead spent blooms to encourage continuous flowering and prevent seed production. Prune back in fall to remove dead or damaged foliage.
- Annual Flowers:Prune as needed to remove wilted blooms and encourage new growth. Deadheading can extend the flowering period.
Post-Trimming Care

Proper aftercare is crucial for the health and vitality of trimmed plants. It involves a combination of watering, fertilizing, and pest control measures to promote healthy growth and prevent infection.
Regular watering is essential to replenish moisture lost during trimming. Water deeply and thoroughly, allowing the water to penetrate the root zone. Avoid overwatering, as this can lead to root rot.
Fertilizing
Fertilizing helps to replenish nutrients removed during trimming. Use a balanced fertilizer diluted to half strength and apply it according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Avoid overfertilizing, as this can burn the roots.
Pest Control
Trimming can expose wounds on plants, making them more susceptible to pests and diseases. Regularly inspect plants for signs of pests or diseases and treat them promptly with appropriate pesticides or fungicides.
Final Conclusion: How To Trim A Plant

By following the principles and techniques Artikeld in this guide, you can transform your plants into thriving specimens that add beauty and vitality to your home or garden. Remember, regular trimming is essential for maintaining healthy growth, preventing disease, and encouraging abundant blooms or fruit production.
Embrace the art of plant trimming and witness the transformative results it brings to your green companions.
FAQ Guide
What are the benefits of trimming plants?
Trimming plants promotes healthy growth, improves their appearance, increases fruit or flower production, and prevents disease.
When is the best time to trim plants?
The optimal time for trimming varies depending on the plant species, but generally, it’s best to trim in late winter or early spring before new growth begins.
What are the different methods of trimming?
Common trimming methods include deadheading (removing spent flowers), thinning (removing excess stems), and shaping (pruning to achieve a desired form).